You don’t have to smoke to get lung cancer anymore. Just living in a polluted area might be enough because air pollution and lung cancer are linked. Every day, millions of people breathe in Delhi’s air, thinking they’re safe as long as they “don’t feel anything.” No cough, no wheeze and no problem, right?
Wrong.
A groundbreaking study just confirmed what doctors feared: air pollution is silently altering your DNA, triggering mutations that can lead to lung cancer, even in lifelong non-smokers. This isn’t hypothetical. It’s happening now, inside your lungs, your child’s lungs, your ageing parents’ lungs — with every breath.
Who should be worried about air pollution and lung cancer?

- Parents of small children
- Fitness enthusiasts who jog in the morning, smog
- Office workers stuck in peak traffic
- Anyone living in a city like Delhi, Noida, or Gurugram
You may not see the damage now, but pollution doesn’t wait for symptoms. It goes straight to your genes.
This blog breaks down how air pollution is rewriting our biology — and what you can do to protect yourself before it’s too late.
So, What Exactly Did the Study Find About Air Pollution and Lung Cancer?
A major analysis of over 870 people across Asia, Europe, and North America found that those exposed to higher levels of PM₂.₅ — the microscopic pollutants smaller than 2.5 microns — were significantly more likely to have cancer-driving mutations in their lung tissue.
These were not smokers. Many had never even been exposed to secondhand smoke. Yet their lungs showed genetic signatures of mutation typically seen in chronic smokers.
Here’s why that’s terrifying:
These mutations can lie dormant for years. But air pollution triggers inflammation, which can “wake up” these mutated cells and start tumor growth.
The Silent Mechanism: What Pollution Does to Your Body?
Let’s break this down simply. Here’s how air pollution harms your body at the genetic level:
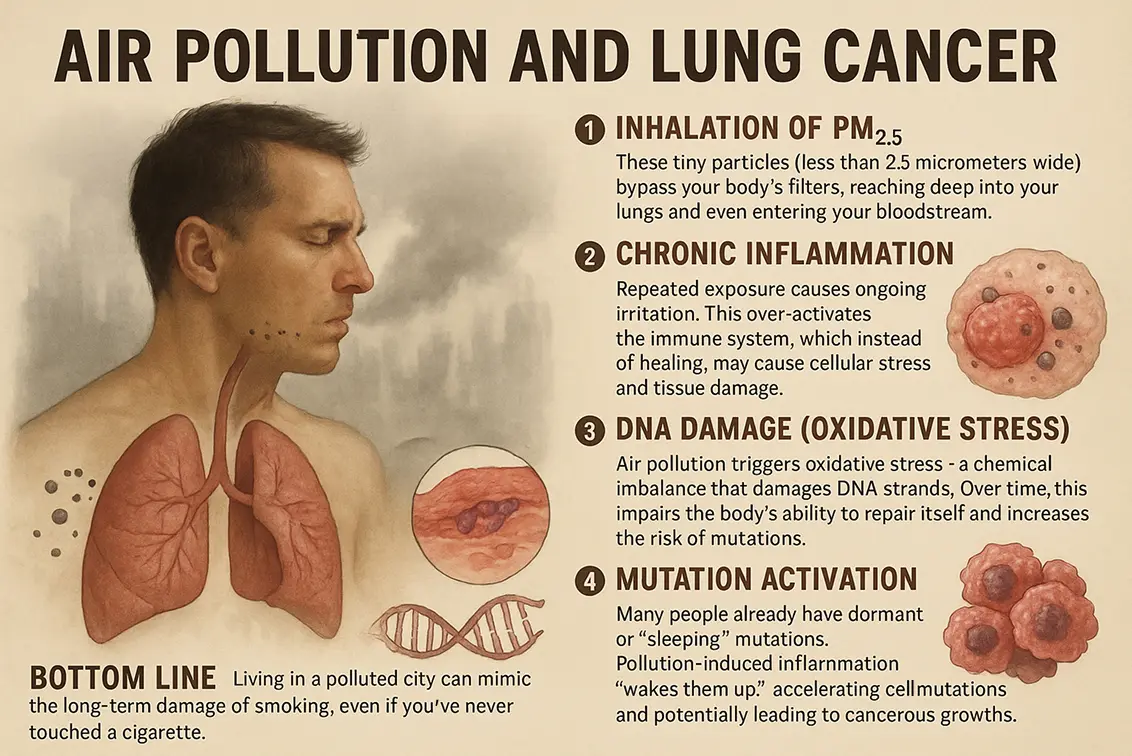
- You inhale PM₂.₅ – These particles are small enough to enter deep into your lungs and even your bloodstream.
- They cause chronic inflammation – Pollution irritates your lungs, causing your immune system to activate repeatedly. Over time, this creates an environment where damaged cells multiply faster.
- Your DNA takes a hit – Pollution exposure leads to oxidative stress, which breaks DNA strands and disrupts natural repair mechanisms. Over time, the damage stacks up.
- Mutation meets inflammation – If you already have “sleeping” mutations (which many people do), the inflammation acts like an alarm clock. It wakes up the mutation and accelerates tumor growth.
In short: You don’t need to be a smoker to have smoker-like lung damage — just a resident of a polluted city.
What does this mean for Delhi, Noida, and Other Most Polluted Cities?

It’s easy to think of pollution as a problem that comes and goes — a bad winter week, a spike in smog, a few days of discomfort. But the truth is far more serious. According to annual air quality data from AQI.in, the pollution in many cities isn’t just an occasional concern — it’s a year-round health hazard.
In 2024, Delhi recorded an average PM2.5 level of 95 µg/m³.
Noida followed closely at 88 µg/m³, and Dhaka at 75 µg/m³.
Now consider this: the World Health Organization’s safe limit for PM2.5 — the fine, lung-penetrating particles most harmful to human health — is just 5 µg/m³.
That means these cities are breathing air that’s 15 to 19 times more polluted than what’s considered safe. Not for a day. Not during a seasonal spike. But on average, across the entire year.
Even when the skies look clearer or the weather feels better, the threat doesn’t go away. The numbers stay dangerously high, silently affecting everyone who steps outside or opens a window.
So what?
That means you’re exposed to multiple pollution spikes every day — enough to keep your immune system inflamed and your DNA under pressure.
The Real Victims: Who’s Most at Risk of Developing Lung Cancer Due to Air Pollution?
1. Children: Kids breathe faster, their lungs are still developing, and they spend more time outdoors. Their cells are more susceptible to DNA mutations — which can mean lifelong consequences.
2. Elderly: Reduced immunity, weak lungs, and existing conditions like asthma or heart disease make seniors extremely vulnerable.
3. Office Goers: Daily commutes in heavy traffic = consistent PM₂.₅ exposure. Plus, poor indoor air quality in offices traps pollutants inside.
4. Fitness Enthusiasts: Running or cycling outdoors when the AQI is even moderate increases inhalation rate, pulling deeper pollutants into the lungs.
Even if you feel healthy now, the damage is cumulative.
Life Expectancy Impact Due to Air Pollution DNA Damage?
According to the Energy Policy Institute at the University of Chicago (EPIC):
Delhi residents are losing up to 7.8 years of life expectancy because of long-term PM₂.₅ exposure. And that’s before accounting for genetic damage.
What You Can Do — Starting Today?
No, you can’t change the city’s air overnight. But you can reduce your exposure and protect your body.
1. Monitor air quality hourly: Use tools like AQI.in, or devices like Prana Air’s indoor/outdoor monitors. Know when it’s unsafe to step outside — and avoid peak pollution times (early morning, late evening traffic).
2. Upgrade your indoor air: Invest in a good HEPA air purifier. Clean air indoors is your first and most effective shield, especially while sleeping.
3. Rethink outdoor activities: Check the AQI before your run. If it’s above 50–75, avoid exertion outdoors.
4. Stay ventilated but smartly: Don’t open windows during high AQI periods. Use exhaust fans and open up only during early morning dips or post-rain periods.
5. Protect children and the elderly: Send kids to school with masks on high-AQI days. Keep grandparents indoors when the AQI spikes.
Final Thoughts: Don’t Wait for Symptoms
Lung cancer doesn’t come with a warning. DNA mutations don’t trigger alarms.
But the evidence is clear: Pollution is no longer just an inconvenience. It’s a daily, invisible attack on your body’s genetic blueprint. Especially, if you live in Delhi NCR, it’s not about “whether” pollution is harming you — it’s about how much damage you can prevent before it’s too late.
Make smarter air choices. Monitor, purify, protect. Because every breath matters — and now, every breath leaves a mark.